Blog by Dr Sam Ahir
An interview with Professor Julian Jones, Professor of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering, Imperial College London.
In the field of regenerative medicine, there is an unmet clinical need for scaffolds that are capable of load sharing alongside host tissue, whilst biodegrading at a predictable rate u...

Shrinkage during UV curing of monomer mixtures is more complex than previously thought, to the extent that the theoretical calculations currently used to predict shrinkage in single monomer mixes by manufacturers formulating their own liquids may no longer apply.
This is according to a paper, Ev...

Increasing business, consumer and regulatory pressures are accelerating the drive for sustainable materials. The plastics and polymer industries are no exception, as the use of natural bio-based monomers derived from renewable biomass resources increases.
Despite the large variety and diversity...
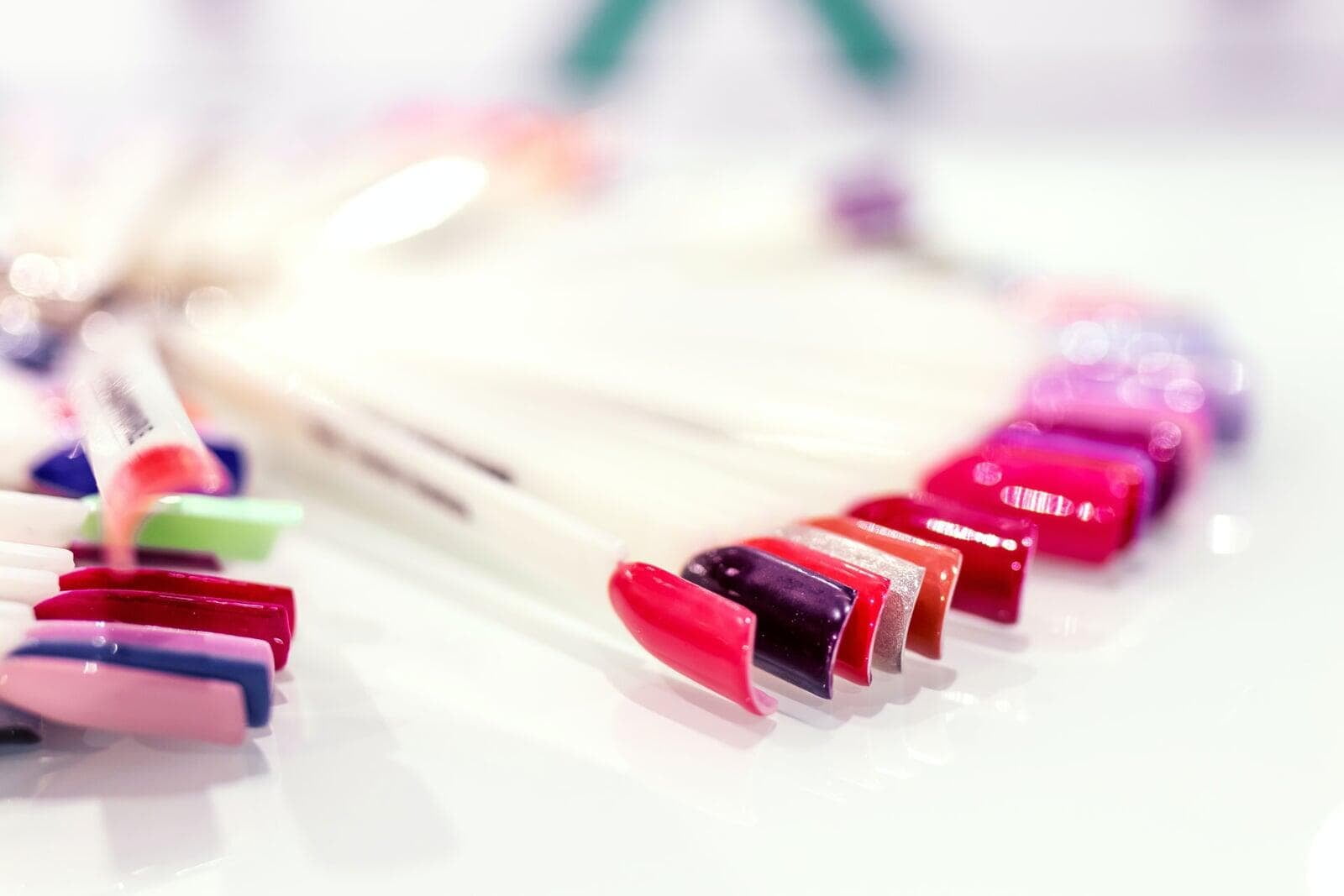


Acrylic nails were originally developed in the 1950s, initially as a spin-out from the dental acrylics industry. The science behind these nails has significantly advanced since then, with the introduction of major product innovations such as the liquid-powder systems in the 1970s, the explosion of c...
Artificial acrylic nails are designed to make the wearer look amazing, whatever the circumstances. Whether dipped or sculpted, the highest quality acrylic nail powders must have fundamental properties that keep the final artificial nails looking beautiful.
These include consistent colour dispersal, c...
Porosity is a big issue in the creation of many acrylic-based products that are manufactured using a powder liquid system. Incorrect powder: liquid ratios and gases, such as air or vaporised excess monomer trapped during polymerisation stages, produces voids or bubbles in the finished product. This ...
In 1987, Per Bak, along with colleagues Tang and Weisenfeld, published a landmark paper in Physics Review Letters (PRL). The paper, Self-organized criticality: An explanation of the 1/f noise, represented a giant leap in the understanding and modelling of dynamical systems. In this article...

Acrylic is a popular choice for many casting and modelling applications, particularly in the production of dental prostheses and cosmetic nails. End users have the relatively simple job of mixing a monomer liquid and a polymer powder to make a dough, which once moulded and cured, forms the desired p...

Poly(methyl methacrylate), commonly abbreviated as PMMA, is one of the most important polymers on the planet. Polymerised using the Methyl methacrylate monomer, PMMA is used in hundreds of applications, each requiring a unique set of characteristics to offer optimum performance.
PMMA is used in every...

Peroxides are highly effective polymerisation initiators and the driving force behind the production of poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) beads. But peroxides are not without their challenges. Peroxide storage and its use must be tightly regulated, both for safety reasons and to ensure polymer ...

Polymerisation inhibitors are crucial for the safe storage of the volatile and easily catalysed methyl methacrylate (MMA). To drive polymerisation during the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), these inhibitors need to be consumed but they leave a chemical footprint. These chemical resid...

Poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is a versatile acrylic plastic. Tough, rigid and transparent, it combines chemical stability with low toxicity for a wide range of industrial and consumer applications. PMMA microbeads are at the heart of many important products, from dental protheses to...

Quality control is the backbone of all manufacturing businesses, driving consistency, compliance and high standards. But this key function is a balancing act, relying on teams to set accurate benchmarks and employ reliable testing procedures. When working with polymers, this involves a detailed know...

Dental prosthetics is a thriving industry, providing innovative solutions to a growing global population, thanks to a range of new materials and techniques. When a successful Australian dental prosthetics manufacturer approached us with a new product, it came with complex chemistry problems. In...